XPLOR Structure Calculations Using AutoStructure: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== <span class="mw-headline"> '''Introduction''' </span> == | == <span class="mw-headline"> '''Introduction''' </span> == | ||
Here we describe the protocol used for performing XPLOR structure calculations in each cycle of AutoStructure version 2.2.1 | Here we describe the protocol used for performing XPLOR structure calculations in each cycle of AutoStructure version 2.2.1 [1]. | ||
== <span class="mw-headline"> '''Protocol''' </span> == | == <span class="mw-headline"> '''Protocol''' </span> == | ||
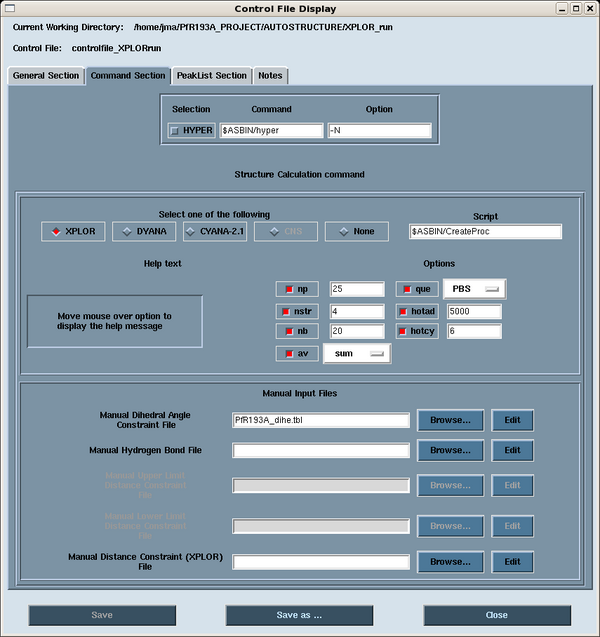
The control file governs the options used in the execution of the AutoStructure run. It is recommended that the user sets these options in the control file using the AutoStructure GUI. The options are found in the Command Section (Figure 1). Select the XPLOR button. The calculations are run over a cluster by a shell script called CreateProc using XPLOR-NIH 2.11.2 | The control file governs the options used in the execution of the AutoStructure run. It is recommended that the user sets these options in the control file using the AutoStructure GUI. The options are found in the Command Section (Figure 1). Select the XPLOR button. The calculations are run over a cluster by a shell script called CreateProc using XPLOR-NIH 2.11.2 [2]. Typically, we compute 100 structures per cycle (i.e., 4 structures in 25 processors), and keep the best 20 structures (lowest energy) for input into the next round of NOESYASSIGN. A queue system (i.e., PBS) is chosen for running over the cluster. The user can select sum or center averaging for treatment of the NOEs. Hotcy is the number of hot cycles in each XPLOR calculation, and hotad is the number of steps at high temperature. Additional files in XPLOR format can be added to the structure calculation in this page, including dihedral angle constraints (_dihe.tbl), hydrogen bond constraints (_hbond.tbl) and manual distance constraints (.tbl). | ||
==== <span class="mw-headline"> Figure 1: AutoStructure Control File: Command Section</span> ==== | ==== <span class="mw-headline"> Figure 1: AutoStructure Control File: Command Section</span> ==== | ||
Here is an example AutoStructure [[Media:Controlfile_XPLORrun.txt|control file]] for an XPLOR run.<span class="mw-headline"> </span><br> | |||
[[Image:AScontrol XPLORcommand.png|600px]] | |||
== '''Starting a Calculation''' == | == '''Starting a Calculation''' == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== '''References''' == | == '''References''' == | ||
1. Huang, Y.J., Tejero, R., Powers, R. and Montelione, G.T. (2006) A topology-constrained distance network algorithm for protein structure determination from NOESY data, ''Proteins 62'', 587-603. | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16374783?itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum&ordinalpos=1 1. Huang, Y.J., Tejero, R., Powers, R. and Montelione, G.T. (2006) A topology-constrained distance network algorithm for protein structure determination from NOESY data, ''Proteins 62'', 587-603.] | ||
2. Schwieters, C.D., Kuszewski, J.J., Tjandra, N. and Clore, G.M. (2003) The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. ''J. Magn. Res. 160'', 65-73. | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12565051?itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum&ordinalpos=2 2. Schwieters, C.D., Kuszewski, J.J., Tjandra, N. and Clore, G.M. (2003) The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. ''J. Magn. Res. 160'', 65-73.] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:34, 6 January 2010
Introduction
Here we describe the protocol used for performing XPLOR structure calculations in each cycle of AutoStructure version 2.2.1 [1].
Protocol
The control file governs the options used in the execution of the AutoStructure run. It is recommended that the user sets these options in the control file using the AutoStructure GUI. The options are found in the Command Section (Figure 1). Select the XPLOR button. The calculations are run over a cluster by a shell script called CreateProc using XPLOR-NIH 2.11.2 [2]. Typically, we compute 100 structures per cycle (i.e., 4 structures in 25 processors), and keep the best 20 structures (lowest energy) for input into the next round of NOESYASSIGN. A queue system (i.e., PBS) is chosen for running over the cluster. The user can select sum or center averaging for treatment of the NOEs. Hotcy is the number of hot cycles in each XPLOR calculation, and hotad is the number of steps at high temperature. Additional files in XPLOR format can be added to the structure calculation in this page, including dihedral angle constraints (_dihe.tbl), hydrogen bond constraints (_hbond.tbl) and manual distance constraints (.tbl).
Figure 1: AutoStructure Control File: Command Section
Here is an example AutoStructure control file for an XPLOR run.
Starting a Calculation
The AutoStructure run is best initiated from the command line in order to perform the structure calculations in parallel. For example:
/farm/software/AutoStructure/AutoStructure-2.2.1/bin/autostructure -c controlfile_XPLORrun -o testXPLORrun.out -v
References