Resonance Assignment/Abacus/FMCGUI objects: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
RyanDoherty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (56 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| | ||
<div>Most of FMCGUI commands operate mainly with the following three objects that are | <div>Most of FMCGUI commands operate mainly with the following three objects that are loaded into computer memory: </div> | ||
*protein sequence | |||
*peak list | |||
*PB fragments | |||
<div> </div> | |||
== '''Protein sequence''' == | == '''Protein sequence''' == | ||
<div> | <div>The protein sequence can be loaded into the program using {[[FMCGUI commands#Data.3EProtein_Sequence.3ELoad|Data>Protein Sequence>Load ]]} or {[[FMCGUI commands#Project.3ELoad|Project>Load]]} commands. <br></div><div>The position ID of the first residue in the sequence should be specified by the user when loading the sequence file (when it is not specified in the input file). Some commands in FMCGUI assume that the first residue of the protein sequence has position ID of 1. Therefore, if there is a HIS-tag, the loaded sequence should be numbered accordingly with a negative position ID for the first residue.</div><div> </div> | ||
== Peak list == | == Peak list == | ||
<div>Different peak lists | <div>Different peak lists can be loaded into the program using {[[FMCGUI commands#Data.3EN15_NOESY.3E|Data>”Peak list name”>Load]]} or {[[FMCGUI commands#Project.3ELoad|Project>Load]]}</div><div></div><div></div><div><br></div> | ||
*(+) peak list needs to be referenced | |||
*(+/-) peak lists could be referenced, but it isn't necessary | |||
*(-) peak lists could be referenced, but it won't be used by FMCGUI<br><span> </span> | |||
{| cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" border="1" | {| cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<div align="center"><span> </span></div><div> </div> | <div align="center"><span> </span></div><div> </div> | ||
== | == List of PB fragments == | ||
<div></div><div>This object can be created in memory using {[[FMCGUI commands# | <div></div><div>This object can be created in memory using {[[FMCGUI commands#Fragment.3ELoad.3EPB_fragments|Fragment>Load>]]}, {[[FMCGUI commands#Fragment.3ECreate.3Eabacus|Fragment>Create>abacus]]}, or {[[FMCGUI commands#Project.3ELoad|Project>Load]]} commands. </div><div></div><div>Each PB fragment in the list has the following main properties:</div> | ||
User ID Fragment ID assigned by user, ''U_id'' | ==== User ID ==== | ||
Fragment ID assigned by user, ''U_id''<span style="font-style: italic">. </span>''U_id'' can’t be changed within FMCGUI. | |||
==== Assignment ID ==== | |||
Assignment ID, ''A_id'', indicates the sequence position ID to which the fragment is assigned.<br> | |||
''A_id'' = -99 if the fragment is not assigned to any position in the sequence. | |||
''A_id'' could be set up or modified by the following commands {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EFix_Assignment.3EManually|Assignment>Fix Assignment>Manually]]}, {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EFix_Assignment.3EUsing_Probability_map|Assignment>Fix Assignment>Using probability Map]]}, and {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EFix_Assignment.3EReset_all|Assignment>Fix Assignment>Reset all]] }. | |||
==== Typing probabilities ==== | |||
<span>T<sup>t </sup>(f) </span><span>is a probability for fragment ''f ''to have amino acid type ''t''</span><span>. Here ''t ''corresponds to one of 20 amino acid residue types, and f </span><span>is fragment user ID. </span> | |||
Typing probbilities can be calculated or modified manually by the commands {[[FMCGUI commands#Fragment.3EType.3ECalculate.3E|Fragment>Type>Calculate]]} and {[[FMCGUI commands#Fragment.3EType.3Efix|Fragment>Type>Fix]]}, respectively. | |||
==== Contact map ==== | |||
:There are three fragment contact maps: C<sup>f1</sup><sub>HNCA</sub><span>(f2) , </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_B</sub><span>(f2) ,</span><span> and </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_F</sub><span>(f2) </span><span>, respectively. Each contact map scores the possibility for any fragment ''f1'' to be next to the fragment ''f2'' in protein sequence. Here ''f''1 and ''f2'' stand for fragment's user ID. </span> | |||
<div><span> Fragment contact map </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>HNCA</sub><span>(f2) </span><span>is calculated based on HNCA spectrum by the command {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EContacts.3EHNCA|Assignment>Contacts>HNCA]]}<div> Fragment<span> contact maps </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_B</sub><span>(f2) </span><span> and </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_F</sub><span>(f2) </span><span> are calculated from NOESY spectra with or without using BACUS procedure, respectively.</span></div><div><span> </span><span> </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_F</sub><span>(f2) </span><span> can be calculated for all values of f1 and f2 by both commands {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EContacts.3ENOE.3Efawn|Assignment>Contacts>NOE>fawn]]} and {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EContacts.3ENOE.3Eabacus|Assignment>Contact>NOE>abacus]]}, while </span>C<sup>f1</sup><sub>NOE_B</sub><span>(f2) </span><span> is calculated by command {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3EContacts.3ENOE.3Eabacus|Assignment>Contact>NOE>abacus]]}.<div> </div></span></div></span></div> | |||
==== Assignment probabilities ==== | |||
| : | ||
<span>P<sup>s</sup>(f) is a probability of fragment f to be assigned to sequense position s, where f is fragment user ID, and s is sequence position ID.</span> <span>There are two assignment probabilities associated with a fragment - P<sup>s</sup><sub>SA</sub>(f) and P<sup>s</sup><sub>REM</sub>(f) - that are calculated using Simulates Annealing (SA) and </span><span>Replica Exchange Method (REM) Monte Carlo simulations, respistively.</span> <span /> | |||
<br> | |||
<div> <span>P<sup>s</sup><sub>SA</sub>(f) is calclated by command {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3ECalculate_Probabilities.3ESA|Assignment>Calculate Probabilities>SA]]} </span><br></div><div>''' '''<span>P<sup>s</sup><sub>REM</sub>(f) is calculated by command {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3ECalculate_Probabilities.3EREM|Assignment>Calculate probabilities>REM]]}.</span></div><div><br></div><div><span>Both assignment probabilities could be also loaded in memory from already performed calculations using command {[[FMCGUI commands#Assignment.3ELoad_Probabilities|Assignment>Load probabilities]]}.</span></div><div> </div><div>'''<br>'''</div> | |||
== Main window == | == Main window == | ||
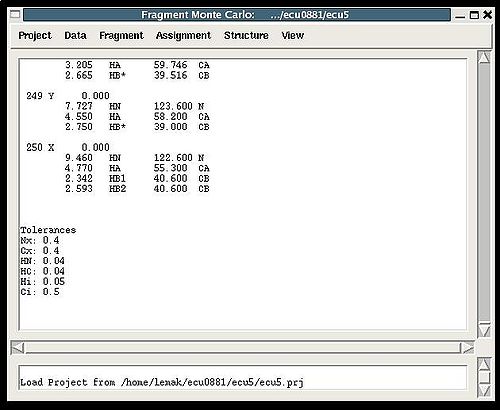
<div></div><div>The main frame of FMC Graphical Interface consist of 4 sections (see Figure | <div></div> | ||
==== Figure 2.1 ==== | |||
<div></div><div>[[Image:Fmcgui mainwindow.jpg|thumb|left|500px]]</div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div></div><div>The main frame of FMC Graphical Interface consist of 4 sections (see Figure)<br></div> | |||
* the title bar displays the name of the current project and the directory inside which the project is located; | |||
* the bar with six menus: [[FMCGUI commands#Project_Menu|Project]], [[FMCGUI commands#Data_Menu|Data]], [[FMCGUI commands#Fragment_menu|Fragment]], [[FMCGUI commands#Assignment_menu|Assignment]], [[FMCGUI commands#Structure_menu|Structure]], and [[FMCGUI commands#View_menu|View]], respectively; | |||
*the project main window, where all messages from the last executed command are displayed ; | |||
*the log window, where the history of executed commands is shown. | |||
<div> </div><div> </div> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:23, 9 January 2010
- protein sequence
- peak list
- PB fragments
Protein sequence
Peak list
- (+) peak list needs to be referenced
- (+/-) peak lists could be referenced, but it isn't necessary
- (-) peak lists could be referenced, but it won't be used by FMCGUI
N15 NOESY
|
-
|
C13 NOESY H2O
|
-
|
Arom NOESY
|
-
|
N15 HSQC
|
+
|
C13 HSQC
|
+
|
HNCA
|
+/-
|
HNCO
|
-
|
CBCACONH
|
+/-
|
HBHACONH
|
+
|
List of PB fragments
User ID
Fragment ID assigned by user, U_id. U_id can’t be changed within FMCGUI.
Assignment ID
Assignment ID, A_id, indicates the sequence position ID to which the fragment is assigned.
A_id = -99 if the fragment is not assigned to any position in the sequence.
A_id could be set up or modified by the following commands {Assignment>Fix Assignment>Manually}, {Assignment>Fix Assignment>Using probability Map}, and {Assignment>Fix Assignment>Reset all }.
Typing probabilities
Tt (f) is a probability for fragment f to have amino acid type t. Here t corresponds to one of 20 amino acid residue types, and f is fragment user ID.
Typing probbilities can be calculated or modified manually by the commands {Fragment>Type>Calculate} and {Fragment>Type>Fix}, respectively.
Contact map
- There are three fragment contact maps: Cf1HNCA(f2) , Cf1NOE_B(f2) , and Cf1NOE_F(f2) , respectively. Each contact map scores the possibility for any fragment f1 to be next to the fragment f2 in protein sequence. Here f1 and f2 stand for fragment's user ID.
Assignment probabilities
Ps(f) is a probability of fragment f to be assigned to sequense position s, where f is fragment user ID, and s is sequence position ID. There are two assignment probabilities associated with a fragment - PsSA(f) and PsREM(f) - that are calculated using Simulates Annealing (SA) and Replica Exchange Method (REM) Monte Carlo simulations, respistively.
Main window
Figure 2.1
- the title bar displays the name of the current project and the directory inside which the project is located;
- the bar with six menus: Project, Data, Fragment, Assignment, Structure, and View, respectively;
- the project main window, where all messages from the last executed command are displayed ;
- the log window, where the history of executed commands is shown.