Resonance Assignment/AutoAssign WebServer: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== '''Introduction''' == | == '''Introduction''' == | ||
In 2009, the members of the Rutgers group (Gautam Singh and Janet Huang) developed a freely accessible web version of AutoAssign, the [[nmr.cabm.rutgers.edu/autoassign|AutoAssign WebServer]]. This web version also provides a consensus approach for automated backbone resonance assignments to take advantage of both [[AutoAssign|AutoAssign]] and [[The PINE Server|PINE]] programs. The AutoAssgin web interface can submit jobs them to both AutoAssign server and PINE web-sever. It will immediately show the results from the AutoAssign server. Once the PINE results are available by e-mail, the user can then upload the PINE result into AutoAssign web interface. The AutoAssign web interface will then show a comparison chart where the user can easily find different resonance assignments between these two programs. This comparison chart can generally guide user for further investigation of resonances assigned differently by AutoAssign and PINE. The resonances assigned by both programs generally have higher accuracy confidences. | |||
<br> | |||
== '''Using the AutoAssign WebServer''' == | == '''Using the AutoAssign WebServer''' == | ||
=== '''AutoAssign''' === | === '''Submitting Jobs to AutoAssign and PINE''' === | ||
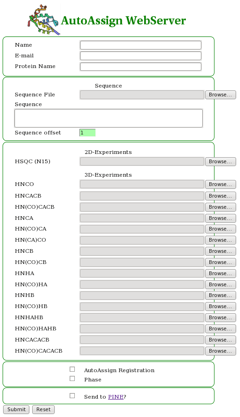
The AutoAssign WebServer interface is quite simple to use (Figure 1). The user uploads the protein sequence file (in single-letter format) and desired peak lists (in Sparky format). Also the user has the option of choosing to perform an AutoAssign registration for setting tolerances, selecting phase if the input data has phase information, and to automateically send the input files to PINE for automated backbone resonance assignment as well (the user will be e-mailed the results from NMRFAM). | |||
==== Figure 1: The AutoAssign WebServer Interface ==== | |||
[[Image:AAwebserver_fig1.png]] | |||
=== AutoAssign WebServer Results === | |||
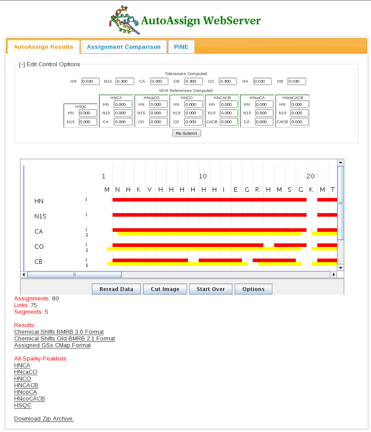
Once the calculations are complete, a results page appears (Figure 2). A connectivity map showing intraresidue (red) and sequential (yellow) assignments is displayed. In the page the user has the option to alter tolerances and global shift parameters and re-run the AutoAssign calculations. Assignment results in BMRB format as well as assigned peak lists for each spectrum in Sparky format can be downloaded from links in the bottom half of the page. | |||
=== | ==== Figure 2: The Results Page ==== | ||
[[Image:AAwebserver_fig2.png]] | |||
=== '''Comparing BMRB Assignments''' === | |||
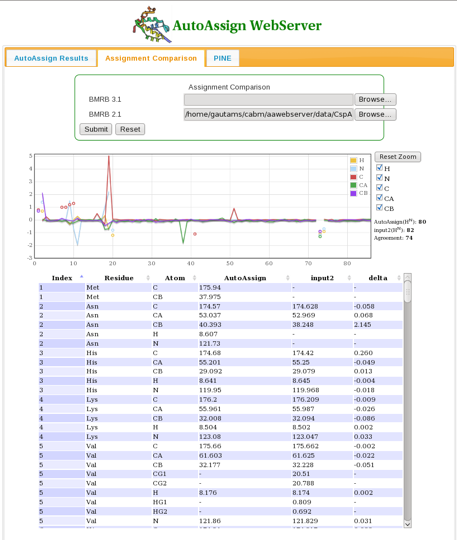
The user can compare chemical shift assignment files in BMRB format using the Assignment Comparison tab (Figure 3). Results showing chemical shift differences for each nucleus are plotted over the entire protein sequence. | |||
==== Figure 3: The Assignment Comparison Page ==== | |||
[[Image:AAwebserver_fig3.png]] | |||
=== '''Stand-Alone Assignment Comparison Tool''' === | |||
Gautam has also written a stand-alone assignment comparison tool which can be accessed on-line at this [http://nmr.cabm.rutgers.edu/autoassign/compare link]. The user uploads bmrb files in either 2.1 or 3.0 format for comparison. At this point, tolerances for comparison of assignments are hard-wired in the code: <sup>1</sup>H, 0.02; <sup>15</sup>N, 0.2; <sup>13</sup>C, . | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
-- Jim Aramini - 10 Nov 2009 | -- Jim Aramini - 10 Nov 2009 | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 10 November 2009
Introduction
In 2009, the members of the Rutgers group (Gautam Singh and Janet Huang) developed a freely accessible web version of AutoAssign, the AutoAssign WebServer. This web version also provides a consensus approach for automated backbone resonance assignments to take advantage of both AutoAssign and PINE programs. The AutoAssgin web interface can submit jobs them to both AutoAssign server and PINE web-sever. It will immediately show the results from the AutoAssign server. Once the PINE results are available by e-mail, the user can then upload the PINE result into AutoAssign web interface. The AutoAssign web interface will then show a comparison chart where the user can easily find different resonance assignments between these two programs. This comparison chart can generally guide user for further investigation of resonances assigned differently by AutoAssign and PINE. The resonances assigned by both programs generally have higher accuracy confidences.
Using the AutoAssign WebServer
Submitting Jobs to AutoAssign and PINE
The AutoAssign WebServer interface is quite simple to use (Figure 1). The user uploads the protein sequence file (in single-letter format) and desired peak lists (in Sparky format). Also the user has the option of choosing to perform an AutoAssign registration for setting tolerances, selecting phase if the input data has phase information, and to automateically send the input files to PINE for automated backbone resonance assignment as well (the user will be e-mailed the results from NMRFAM).
Figure 1: The AutoAssign WebServer Interface
AutoAssign WebServer Results
Once the calculations are complete, a results page appears (Figure 2). A connectivity map showing intraresidue (red) and sequential (yellow) assignments is displayed. In the page the user has the option to alter tolerances and global shift parameters and re-run the AutoAssign calculations. Assignment results in BMRB format as well as assigned peak lists for each spectrum in Sparky format can be downloaded from links in the bottom half of the page.
Figure 2: The Results Page
Comparing BMRB Assignments
The user can compare chemical shift assignment files in BMRB format using the Assignment Comparison tab (Figure 3). Results showing chemical shift differences for each nucleus are plotted over the entire protein sequence.
Figure 3: The Assignment Comparison Page
Stand-Alone Assignment Comparison Tool
Gautam has also written a stand-alone assignment comparison tool which can be accessed on-line at this link. The user uploads bmrb files in either 2.1 or 3.0 format for comparison. At this point, tolerances for comparison of assignments are hard-wired in the code: 1H, 0.02; 15N, 0.2; 13C, .
-- Jim Aramini - 10 Nov 2009